In the rapidly evolving field of medicine, what may have been accepted as truth yesterday can be debunked by the research of today. This constant advancement leads to the discrediting of many long-held beliefs. Exploring these changes is not just an academic exercise—it helps prevent the spread of misinformation and encourages informed health decisions. Let’s take a journey through the past century to debunk ten medical myths that science has laid to rest.
1. Vaccines Cause Autism
In the late 1990s, a study published by a British surgeon proposed a link between the MMR vaccine (measles, mumps, and rubella) and autism. This claim has been thoroughly debunked by numerous large-scale studies which found no credible evidence to support the connection. The original study was retracted, and the author lost his medical license, but the myth persists, affecting vaccination rates and public health.
2. Teething Causes Fever in Babies
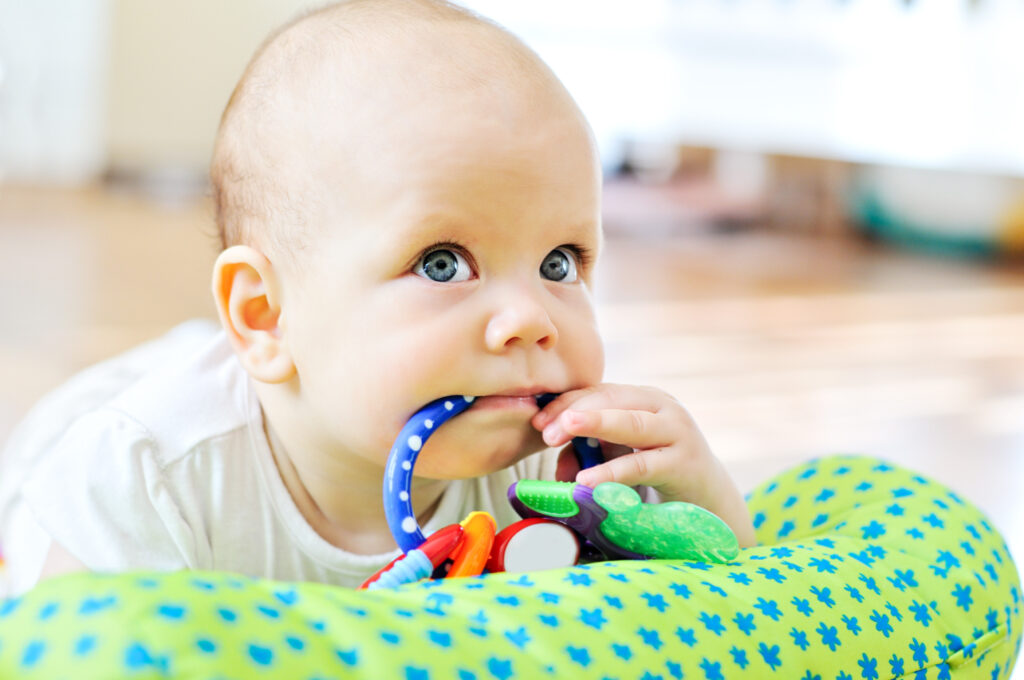

A common misconception is that teething causes a significant fever in babies. While teething might make babies more irritable and cause a slight increase in their temperature, it does not cause a high fever. Studies have shown that high fevers are typically caused by infections and other illnesses, not by teething. Parents should seek medical advice if their child has a high fever, rather than attributing it to teething.
3. Reading in Dim Light Ruins Your Eyesight

The belief that reading in dim light can ruin your eyesight has been a common warning from parents to children. However, scientific studies indicate that while reading in low light might strain your eyes and cause temporary discomfort, it does not cause permanent damage to your eyesight. Good lighting can make reading more comfortable, but the effects of poor lighting are not as dire as once feared.
4. Eating Chocolate Causes Acne

The idea that chocolate directly causes acne is a persistent myth. While diet can affect the skin, no scientific study has conclusively linked the consumption of chocolate with an increase in acne. More recent research suggests that high glycemic index foods and dairy products may influence skin health, but chocolate alone is not the culprit.
5. You Lose Most Body Heat Through Your Head

The claim that humans lose the majority of their body heat through their heads was based on a flawed interpretation of a military study. Later research demonstrated that the head, while significant, is no more likely to lose heat than any other uncovered part of the body. Proper clothing and protection are required in cold temperatures for all exposed skin, not just the head.
6. Ulcers Are Caused Solely By Stress
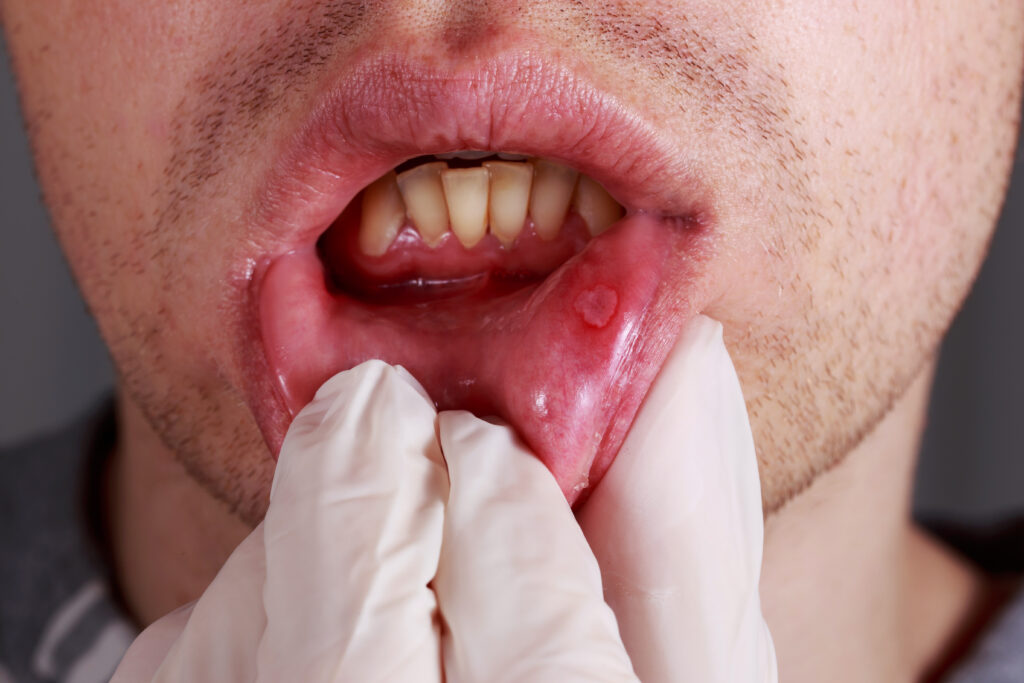
For many years, it was believed that ulcers were caused by stress and spicy food. It wasn’t until the late 20th century that researchers identified Helicobacter pylori bacteria as a primary cause of most stomach ulcers. This discovery shifted treatment from stress reduction and diet modification to antibiotic therapy, significantly improving outcomes for ulcer patients.
7. Cracking Your Knuckles Causes Arthritis

The habit of cracking knuckles has long been rumored to lead to arthritis. However, numerous studies have shown that there is no direct correlation between knuckle cracking and the development of arthritis. The sound heard is caused by the popping of gas bubbles in the joint fluid, a harmless process.
8. Shaved Hair Grows Back Thicker

Many believe that shaving unwanted hair causes it to grow back thicker and coarser. Scientific evaluation, however, demonstrates that shaving does not affect the thickness or rate of hair regrowth. This misconception arises from the blunt tip of the regrowing hair feeling coarser compared to the naturally tapered end of unshaven hair.
9. Sitting Too Close to the Television Damages Eyesight

This myth originated from concerns about radiation from old cathode ray tube (CRT) televisions, which could emit low levels of radiation. With modern televisions, especially LCD, LED, and Plasma screens, this concern is no longer relevant. Sitting close to the TV may cause eyestrain or fatigue, but it does not permanently damage vision.
10. Eight Glasses of Water a Day

While staying hydrated is crucial for health, the rule that everyone should drink eight glasses of water daily is not supported by scientific evidence. Hydration needs vary depending on the individual’s age, activity level, and environment. It’s more important to drink when you are thirsty and consider all fluid intake, including food and other beverages.
The Evolution of Medical Knowledge

Understanding the evolution of medical knowledge helps debunk myths and encourages more scientifically sound health practices. By staying informed through reliable sources and ongoing research, we can ensure that our health decisions are based on facts rather than outdated beliefs. As science progresses, it is crucial to keep questioning and learning, which ultimately leads to better health outcomes and a more informed public.

